Delving into the macromolecules worksheet #2 answer key, we embark on a captivating journey into the realm of these complex molecules that form the very foundation of life. From their intricate composition to their diverse applications, this comprehensive guide unravels the secrets of macromolecules, empowering students and researchers alike to grasp their fundamental significance.
As we navigate through the intricacies of macromolecules, we will decipher their composition, unravel the concepts underlying each worksheet question, and delve into the reasoning behind the provided answers. Furthermore, we will explore the educational value of this worksheet, highlighting its role in fostering a deeper understanding of macromolecules.
Macromolecules
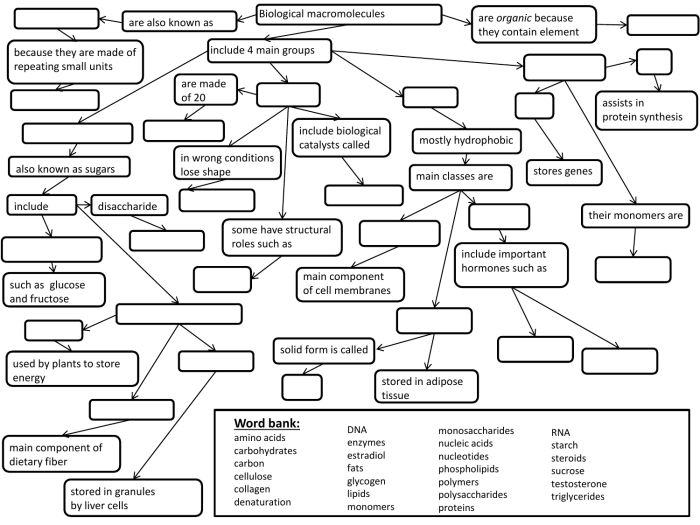
Macromolecules are large molecules composed of many smaller molecules called monomers. They play crucial roles in various biological processes and are essential for life.
Composition of Macromolecules
Macromolecules are composed of monomers linked together by covalent bonds. The types of monomers and the bonds that connect them determine the structure and function of the macromolecule. The four main types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Examples of Different Types of Macromolecules, Macromolecules worksheet #2 answer key
- Carbohydrates: Composed of sugar monomers (e.g., glucose, fructose) linked by glycosidic bonds. Examples include starch, cellulose, and glycogen.
- Lipids: Composed of fatty acid monomers linked by ester bonds. Examples include triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids.
- Proteins: Composed of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. Examples include enzymes, hormones, and antibodies.
- Nucleic acids: Composed of nucleotide monomers linked by phosphodiester bonds. Examples include DNA and RNA.
User Queries: Macromolecules Worksheet #2 Answer Key
What are the main types of macromolecules?
The four main types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is the function of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates provide energy and structure to cells.
What is the difference between a monomer and a polymer?
A monomer is a single unit of a macromolecule, while a polymer is a chain of monomers.