Area of triangles and other polygons iready – Embark on a journey into the realm of geometry as we explore the fascinating topic of area of triangles and other polygons. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of polygon area calculations, equipping you with the knowledge and understanding to navigate this essential mathematical concept.
From the fundamental formulas for triangles to the more complex calculations for various polygons, we will unravel the secrets of polygon area determination. Prepare to expand your geometric horizons as we uncover the practical applications of these formulas in diverse fields, empowering you to solve real-world problems with precision and confidence.
Area of Triangles
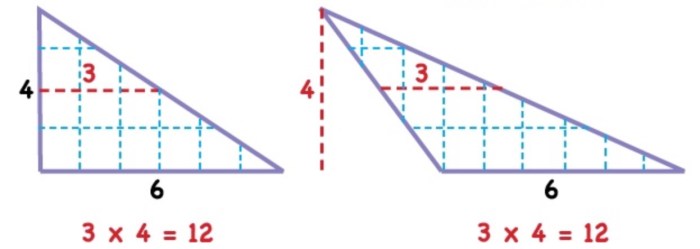
The area of a triangle is calculated using the formula: A = 1/2 – base – height. The base is the length of one side of the triangle, and the height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex.
This formula applies to all types of triangles, including equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles.
For example, to find the area of a triangle with a base of 6 cm and a height of 4 cm, we use the formula: A = 1/2 – 6 cm – 4 cm = 12 cm 2.
Relationship between Base, Height, and Area, Area of triangles and other polygons iready
The area of a triangle is directly proportional to both its base and height. This means that if you double the length of the base, the area will double. Similarly, if you double the height, the area will also double.
This relationship can be seen in the formula: A = 1/2 – base – height. If we increase the base by a factor of k, the area will increase by the same factor k. Similarly, if we increase the height by a factor of k, the area will also increase by the factor k.
Area of Other Polygons
The area of other polygons can be calculated using different formulas depending on the type of polygon.
Rectangles
The area of a rectangle is calculated using the formula: A = length – width.
Squares
The area of a square is calculated using the formula: A = side 2.
Parallelograms
The area of a parallelogram is calculated using the formula: A = base – height.
Trapezoids
The area of a trapezoid is calculated using the formula: A = 1/2 – (base1 + base2) – height.
Circles
The area of a circle is calculated using the formula: A = π – radius 2.
Applications of Polygon Area Formulas
Polygon area formulas have numerous applications in real-world fields such as architecture, engineering, and design.
Architecture
Architects use polygon area formulas to calculate the floor area of buildings, the surface area of walls, and the volume of rooms.
Engineering
Engineers use polygon area formulas to calculate the area of cross-sections of beams, the surface area of heat exchangers, and the volume of tanks.
Design
Designers use polygon area formulas to calculate the area of fabric needed for curtains, the surface area of furniture, and the volume of packaging.
Advanced Topics in Polygon Area: Area Of Triangles And Other Polygons Iready
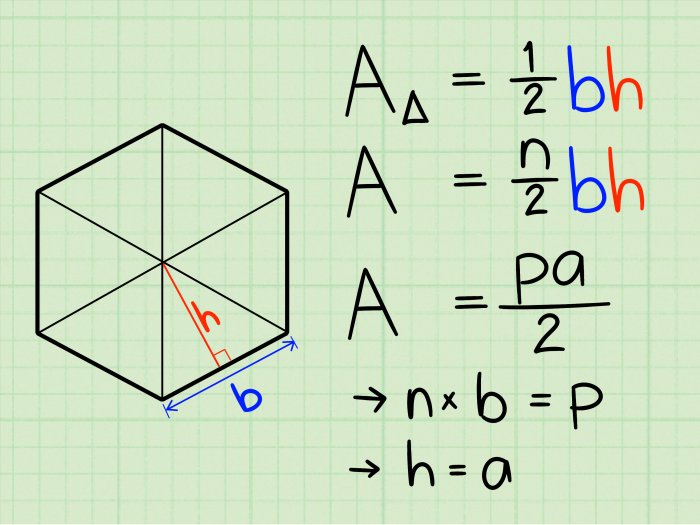
Centroid
The centroid of a polygon is the point where all the medians intersect. The centroid divides the polygon into two equal areas.
Circumradius
The circumradius of a polygon is the radius of the circle that passes through all the vertices of the polygon.
Inradius
The inradius of a polygon is the radius of the circle that is inscribed in the polygon, meaning it touches all the sides of the polygon.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software
CAD software uses polygon area formulas to calculate the area of complex shapes. This software is used in a variety of industries, including architecture, engineering, and manufacturing.
General Inquiries
What is the formula for calculating the area of a triangle?
Area = (1/2) – base – height
How can I find the area of a polygon that is not a triangle?
The area of a polygon can be calculated using various formulas depending on the specific type of polygon. Some common formulas include those for rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and circles.
What are some real-world applications of polygon area formulas?
Polygon area formulas find applications in architecture, engineering, design, land surveying, and many other fields where precise measurement of geometric shapes is crucial.