Embark on a captivating journey into the microscopic realm with the Cell Structure Function Crossword Answer Key. This comprehensive guide unlocks the mysteries of cellular life, deciphering the intricate relationship between a cell’s structure and its diverse functions.
Delve into the fundamental building blocks of cells, exploring the specialized roles of organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes. Discover how the cell membrane governs the vital processes of nutrient uptake and waste elimination. Witness the remarkable dance of cell division, driving growth, repair, and the perpetuation of life.
Cell Structure and Function Overview
Cells are the fundamental unit of life and perform various functions essential for the survival and functioning of living organisms. Understanding cell structure and function is crucial for comprehending the complexity of life processes. This article provides an overview of the basic structure of cells, their organelles, and their respective functions.
Cells are composed of a variety of organelles, each with specialized functions. The nucleus, the control center of the cell, contains the genetic material (DNA). Mitochondria generate energy through cellular respiration. Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis. The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein folding and lipid metabolism.
The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins for secretion. Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes and play a role in cellular waste disposal. Vacuoles are storage compartments that can contain various substances, such as water, ions, or nutrients.
The relationship between cell structure and function is evident in the diversity of cells found in different organisms. For instance, muscle cells have specialized structures called myofibrils that allow for muscle contraction. Nerve cells have long extensions called axons that transmit electrical signals.
Plant cells have a cell wall that provides structural support and protection. These specialized structures enable cells to perform their unique functions and contribute to the overall functioning of the organism.
Organelles and Their Functions: Cell Structure Function Crossword Answer Key
| Organelle | Structure | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Membrane-bound compartment containing DNA | Controls cellular activities, stores genetic information | Found in all eukaryotic cells |
| Mitochondria | Double-membrane bound organelles | Produce energy through cellular respiration | Found in most eukaryotic cells |
| Ribosomes | Small, non-membrane bound organelles | Protein synthesis | Found in all cells |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Network of interconnected membranes | Protein folding, lipid metabolism | Found in eukaryotic cells |
| Golgi Apparatus | Stack of flattened membranes | Modifies and packages proteins for secretion | Found in eukaryotic cells |
| Lysosomes | Membrane-bound organelles containing digestive enzymes | Cellular waste disposal | Found in eukaryotic cells |
| Vacuoles | Membrane-bound compartments | Storage of water, ions, nutrients | Found in both plant and animal cells |
Cell Membrane and Transport
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The cell membrane regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell, maintaining the cell’s internal environment.
Membrane transport occurs through various mechanisms, including passive diffusion, active transport, and endocytosis. Passive diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without energy expenditure. Active transport is the movement of molecules against a concentration gradient, requiring energy from ATP.
Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in large molecules or particles by engulfing them into vesicles.
Membrane transport is essential for cell function. It allows cells to take in nutrients, expel waste products, and maintain the appropriate concentrations of ions and molecules within the cell.
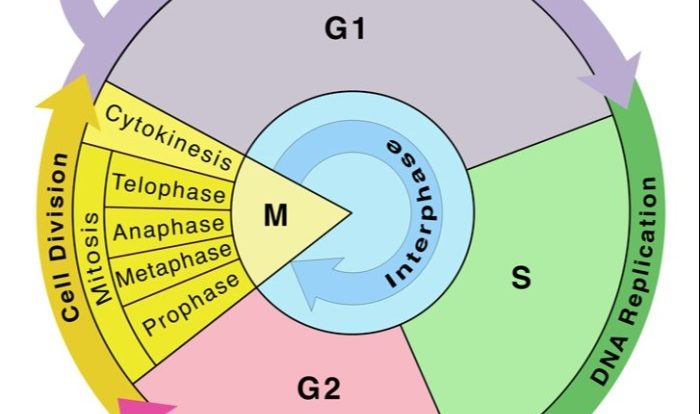
Cell Division and Reproduction
Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two or more daughter cells. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. It occurs in somatic cells (non-reproductive cells) and is essential for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
Meiosis is the process by which a cell divides into four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It occurs in reproductive cells (gametes) and is essential for sexual reproduction.
Cell division is a fundamental process that ensures the continuity of life and the maintenance of genetic information.
Cell Communication and Signaling
Cells communicate with each other through a variety of signaling mechanisms. These mechanisms allow cells to coordinate their activities and respond to changes in the environment.
There are three main types of cell signaling: paracrine, endocrine, and autocrine signaling.
Paracrine signaling occurs when a cell releases a signaling molecule that affects nearby cells.
Endocrine signaling occurs when a cell releases a signaling molecule that travels through the bloodstream to reach target cells in distant parts of the body.
Autocrine signaling occurs when a cell releases a signaling molecule that binds to receptors on the same cell.
Cell signaling is essential for coordinating cell activities, maintaining homeostasis, and responding to external stimuli.
FAQ Summary
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
Regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
How do ribosomes contribute to cell function?
Protein synthesis, essential for cell growth and repair.
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse daughter cells.