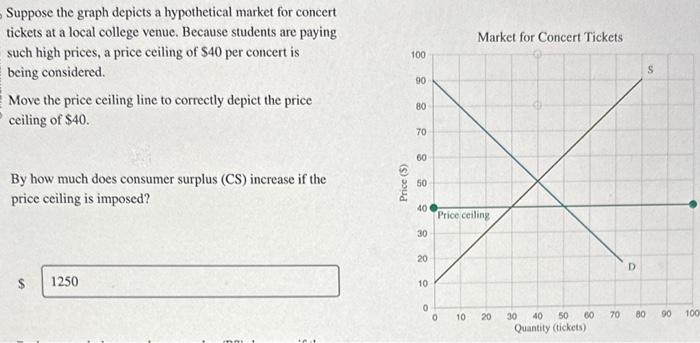
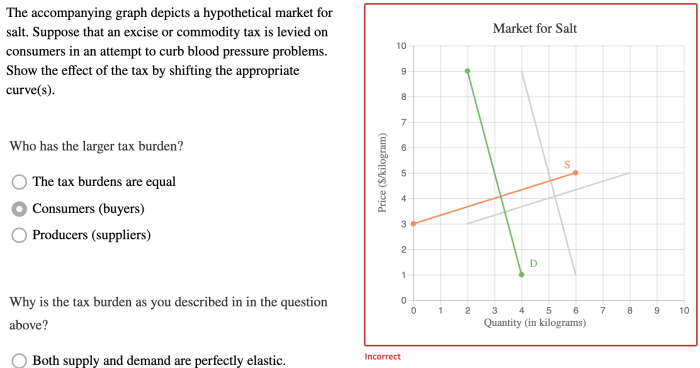
Suppose the graph depicts a hypothetical market, a realm where supply and demand dance in a delicate balance, determining the equilibrium price and quantity. This narrative delves into the intricacies of market dynamics, exploring the shifts and interventions that shape the economic landscape.
As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the forces that drive market equilibrium, examining how changes in supply or demand can disrupt this delicate balance. We will dissect the concept of market disequilibrium, its causes and consequences, and delve into the role of government interventions in shaping market outcomes.
Market Equilibrium
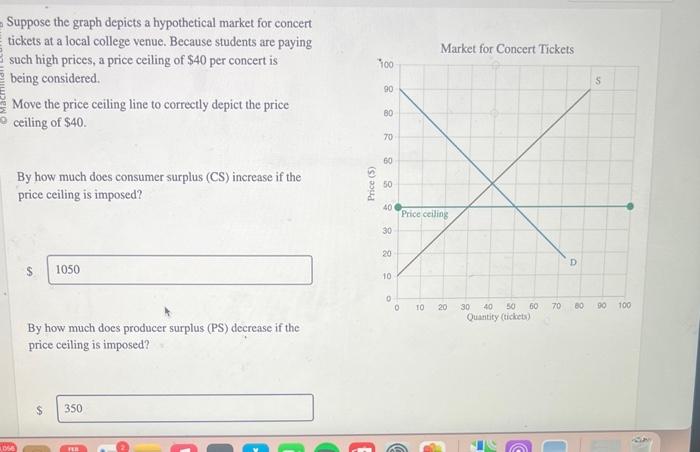
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied in a market equals the quantity demanded, resulting in a stable price and quantity.
At equilibrium, supply and demand curves intersect. The equilibrium price is the price at which buyers are willing to purchase the quantity supplied by sellers, and the equilibrium quantity is the amount purchased and sold at that price.
Shifts in Supply and Demand
Changes in supply or demand can shift the equilibrium point.
| Shift | Effect on Equilibrium Price | Effect on Equilibrium Quantity | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increase in Supply | Decrease | Increase | Technological advancement |
| Decrease in Supply | Increase | Decrease | Natural disaster |
| Increase in Demand | Increase | Increase | New product launch |
| Decrease in Demand | Decrease | Decrease | Change in consumer preferences |
Market Disequilibrium
Market disequilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied is not equal to the quantity demanded.
Surpluses occur when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded, leading to a price decrease. Shortages occur when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied, leading to a price increase.
Government Intervention
Governments may intervene in markets to influence market equilibrium.
- Price Ceilings: Set a maximum price, creating a surplus.
- Price Floors: Set a minimum price, creating a shortage.
- Subsidies: Reduce the cost of production, increasing supply.
- Taxes: Increase the cost of production, decreasing supply.
Real-World Examples, Suppose the graph depicts a hypothetical market
- Housing Market: Supply and demand shifts due to economic downturns or population growth.
- Oil Market: Supply and demand affected by political instability or technological advancements.
- Healthcare Market: Demand increases due to aging population, supply limited by physician availability.
Answers to Common Questions: Suppose The Graph Depicts A Hypothetical Market
What is market equilibrium?
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity of a good or service supplied in a market is equal to the quantity demanded at a specific price.
How can shifts in supply or demand affect market equilibrium?
Shifts in supply or demand can lead to changes in the equilibrium price and quantity, depending on the direction and magnitude of the shift.
What is market disequilibrium?
Market disequilibrium occurs when the quantity of a good or service supplied is not equal to the quantity demanded at a specific price.