Which of the following is true of neuroleptic drugs? These medications, commonly known as antipsychotics, play a pivotal role in the treatment of mental health conditions, particularly psychosis. Understanding their effects on neurotransmitters, clinical applications, side effects, and mechanisms of action is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking information about these drugs.
Neuroleptic drugs exert their therapeutic effects by modulating dopamine and serotonin levels in the brain. They are primarily used to manage symptoms of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other psychotic conditions. However, their use is not without potential risks, including side effects such as extrapyramidal symptoms and tardive dyskinesia.
Careful monitoring and management are essential to ensure optimal outcomes and minimize adverse effects.
Effects on Neurotransmitters

Neuroleptic drugs primarily exert their therapeutic effects by modulating neurotransmitter activity in the brain, particularly dopamine and serotonin.
Dopamine dysregulation is strongly implicated in the pathophysiology of psychosis. Neuroleptic drugs act as dopamine antagonists, blocking dopamine receptors in the mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways. This results in a decrease in dopaminergic activity, which can alleviate the positive symptoms of psychosis, such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
Serotonin also plays a role in the regulation of mood and behavior. Some neuroleptic drugs have serotonin receptor antagonist properties, which can contribute to their mood-stabilizing effects and may be beneficial in treating negative symptoms of psychosis, such as social withdrawal and apathy.
Clinical Uses
Neuroleptic drugs are commonly used to treat a range of mental health conditions, including:
Schizophrenia
- Positive symptoms: hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking
- Negative symptoms: social withdrawal, apathy, anhedonia
Bipolar Disorder, Which of the following is true of neuroleptic drugs
- Manic episodes: elevated mood, racing thoughts, decreased need for sleep
- Depressive episodes: low mood, anhedonia, fatigue
Other Conditions
- Tourette’s syndrome: tics, involuntary movements
- Anxiety disorders: generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Nausea and vomiting: as antiemetics
Side Effects and Risks: Which Of The Following Is True Of Neuroleptic Drugs
Neuroleptic drugs can cause a range of side effects, including:
Common Side Effects
- Extrapyramidal symptoms: tremors, rigidity, akathisia
- Sedation
- Anticholinergic effects: dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention
- Weight gain
Long-Term Risks
Tardive dyskinesia is a serious potential complication of long-term neuroleptic drug use. It is characterized by involuntary, repetitive movements of the face, mouth, and limbs.
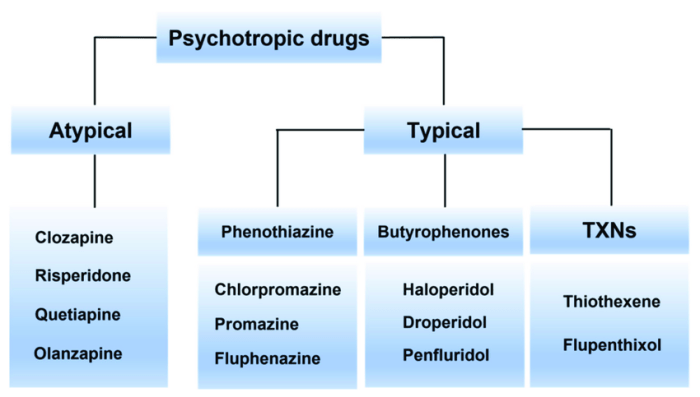
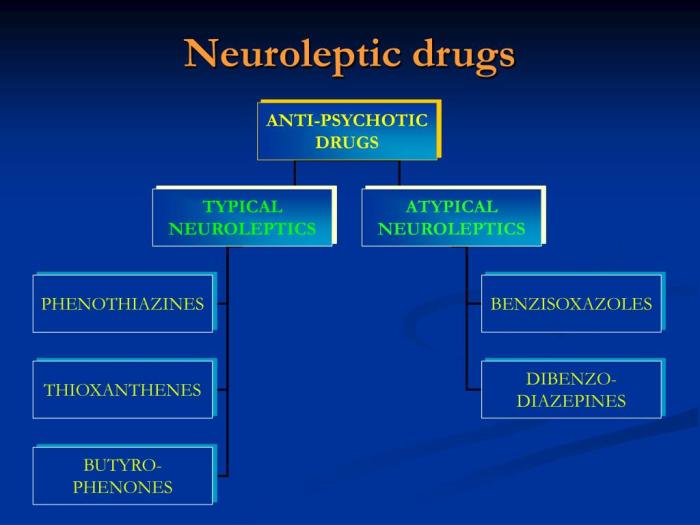
Types and Mechanisms of Action
Neuroleptic drugs can be classified into different types based on their chemical structure and mechanism of action:
| Type | Chemical Structure | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Neuroleptics (First-Generation) | Phenothiazines, butyrophenones | Dopamine receptor antagonists |
| Atypical Neuroleptics (Second-Generation) | Clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone | Mixed dopamine and serotonin receptor antagonists |
Atypical neuroleptics generally have a lower risk of extrapyramidal side effects compared to typical neuroleptics due to their broader receptor affinity profile.
Dosing and Administration
The appropriate dosage of neuroleptic drugs varies depending on the individual patient, the condition being treated, and the specific drug being used.
Neuroleptic drugs can be administered orally, intramuscularly, or intravenously. Oral administration is the most common route, while intramuscular and intravenous administration may be used in acute situations or for patients who cannot tolerate oral medication.
Monitoring and Management
Regular monitoring is essential during neuroleptic drug treatment to ensure efficacy and minimize adverse effects.
Parameters that should be monitored include:
- Clinical response
- Side effects
- Blood levels (for some drugs)
If adverse effects occur, dose adjustments or switching to a different medication may be necessary.
Popular Questions
What are the most common side effects of neuroleptic drugs?
Extrapyramidal symptoms, such as tremors, rigidity, and akathisia, are common side effects.
Can neuroleptic drugs cause long-term risks?
Yes, tardive dyskinesia, a movement disorder, is a potential long-term risk.
How are neuroleptic drugs typically administered?
Oral administration is the most common route, but intramuscular injection may be used in acute situations.